Introduction

Normally when we design an antenna we have to calculating the size of the antenna with respect to the wavelength of the desired frequency. “Half-wavelength Dipole Antenna” specified, we should make the antenna length equal to half of the wavelength in resonance frequency.
This for 5GHz we need to use extremely small antenna sizes, about 0.06 meters or 6 millimeters. To design an antenna which resonates with 100MHz frequency requires 3 meters length.
But let’s think about the no-length antenna and let’s talk about the degrees instead of length. As the picture shown on the left hand side we have two patches and they have a number of degrees between each other. Bow-tie antennas provides wide-range of bandwidth [1].

There are many types of bow-tie antenna:
- Wideband Printed Bowtie Antenna
- Bowtie Slot Antenna
- Double-sided Triangular Bowtie Antenna
- Bowtie Microstrip Fed Antenna
- Slotted Bowtie Patch Antenna
- CPW Fed Curved Bowtie Slot Antenna
This type of antennas are widely used for UHF ranges, thanks to its gain and its wide bandwidth [2].
Basic Calculations
There are different types of calculations for this type of antenna. One of those provides the following equations:
width (cm) = 7200 / MHz
height (cm) = 2900 / MHz
The distance between the two triangles can be between 5mm and 2 cm, also in relation to the operating frequency. Another more precise formula provides the following calculations:
width (mm) = 0.375 * Lambda * 1000;
height (mm) = 0.25 * λ* 1000;
distance (mm) = 0.02066 * λ * 1000.
Let’s analyze the most general form of bowtie antenna [2].
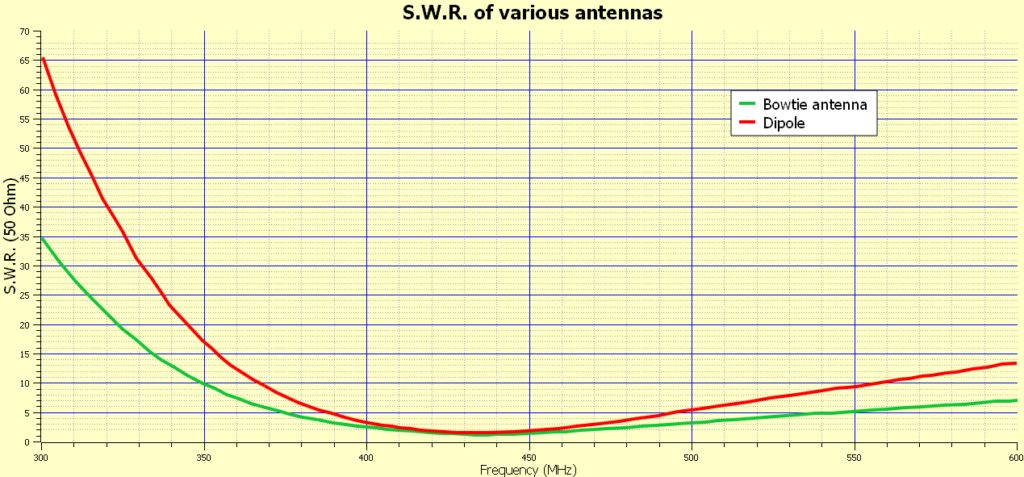
As you can see it provides wide range of VSWR when compared with the dipole antenna.

We can increase the gain of resonant frequency or make it multiband antenna with adding slit and slots. Also there are another methods to increase the gain, VSWR, radiation pattern, etc.
But let’s examine the slit and slot methods to understand deeply the bow-tie antennas.
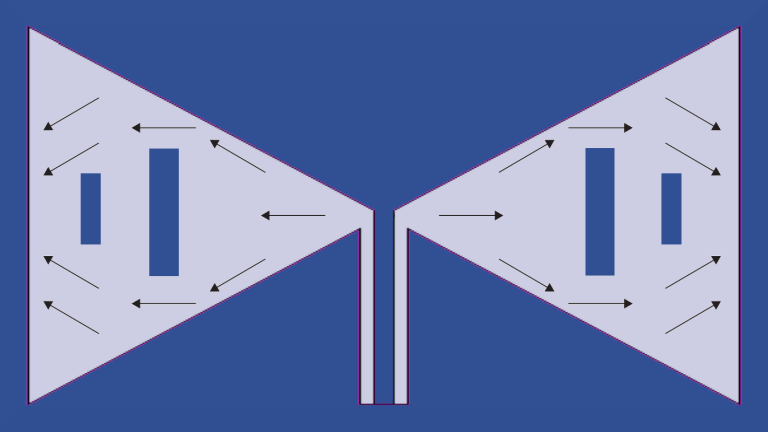
Spit and Slit
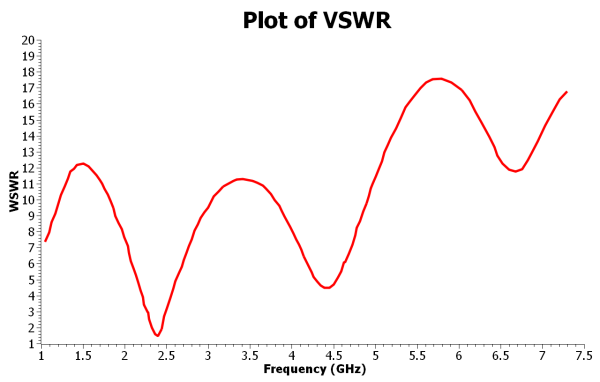
Different types of geometries effects the antennas gain, resonance frequency, number of resonance frequencies, VSWR value, etc. Broadband antennas can resonate in different frequencies with high gain values. And there are some ways to change broadband performance:
- Increasing the resonance frequencies.
- Modifying the antenna geometry.
- Modifying the substrate parameters of the structure of the antenna.
For more detailed information you can check the Kin-Lu Wong’s Compact and Broadband Microstrip Antennas [3].
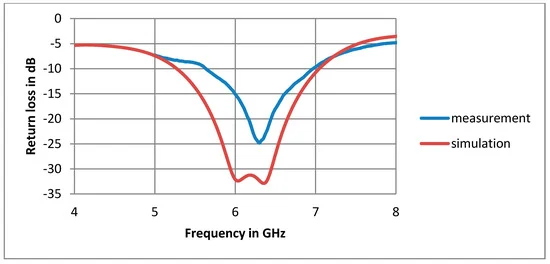
As you can see the antenna resonates perfectly at 2.45GHz and VSWR value is very low. At other frequencies, we can easily see the poor performance of the antenna. Thanks for the Giovanni Di Maria’s excellent work [2].
Bow-tie antennas can be used with modern wireless applications like mobile phones. Here are the some applications of bow-tie antennas [5]:
- 5G, base stations of cell phones.
- UWB applications such as GPR, Wi-Fi, wireless, etc.
- Short-Range Radars
Bibliography
[1]: https://www.antenna-theory.com/antennas/wideband/bowtie.php
[2]: https://www.eeweb.com/slotted-bowtie-antenna/
[3]: Amar, Ahmed. (2020). Re: What is an antenna design technique to get a broadband frequency result?. Retrieved from: https://www.researchgate.net/post/What-is-an-antenna-design-technique-to-get-a-broadband-frequency-result/5f836faf6e357838693e2270/citation/download.
[4]: https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/10/2/504
[5]: https://www.elprocus.com/bow-tie-antenna/
Featured Image: https://www.electro-tech-online.com/threads/16-bow-tie-tv-antenna.159775/

Leave a Reply